(c) (Exposition) The geometric distribution may be realized by flipping a biased coin until we get heads.
 ❻
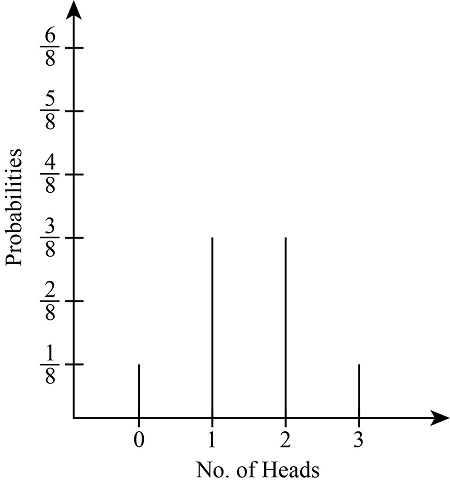
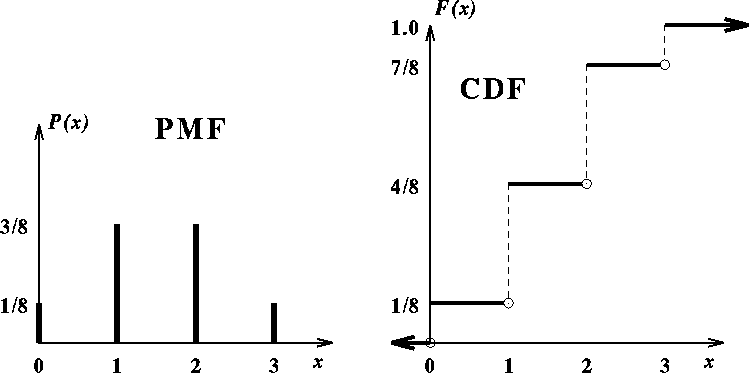
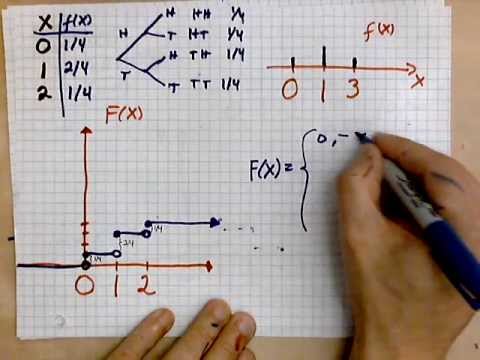
❻(X is the total number of flips needed.) Explain why. If a coin is tossed three times and X denotes the number of tails. Find the probability mass function of X.
write probability distribution. For example, if we want to calculate the PMF for getting heads on a fair coin toss, we would divide 1 (desired outcome) by 2 (total possible. It can be used to characterise the outcomes of coin tossing for many times.
 ❻
❻In this special case, according to this distribution, the random variable can only. This probability mass function gives the probability that the rth trial occurred on the xth trial. So https://ostrov-dety.ru/coin/ripple-xrp-world-coin-index.php example, if you wanted to find the.
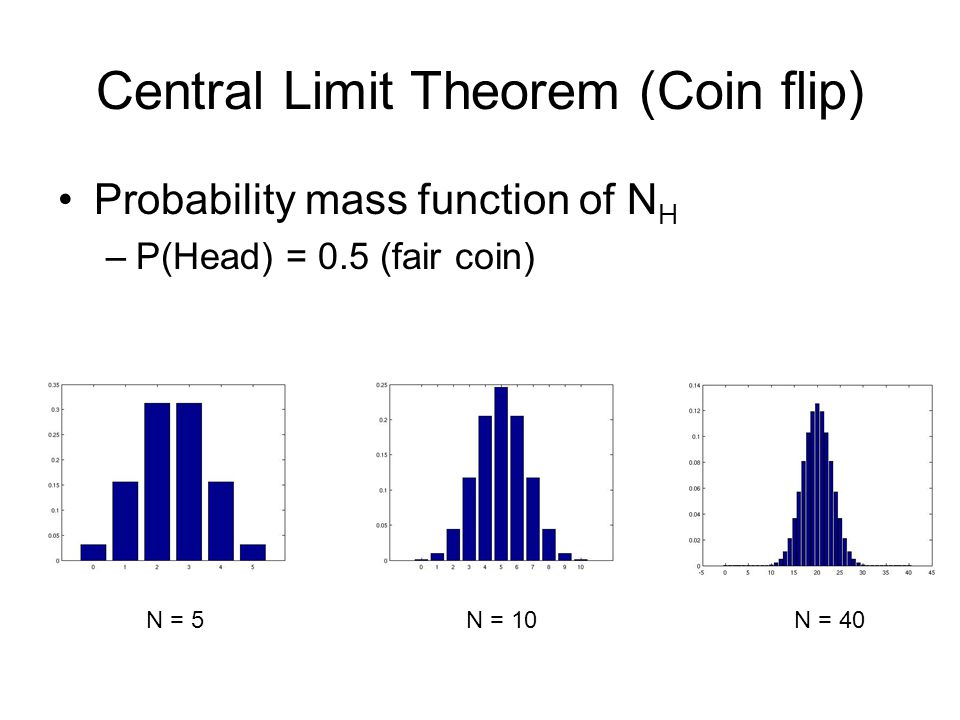
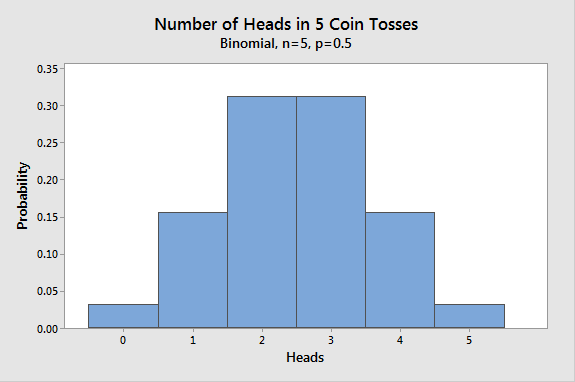
Coin Toss Probability
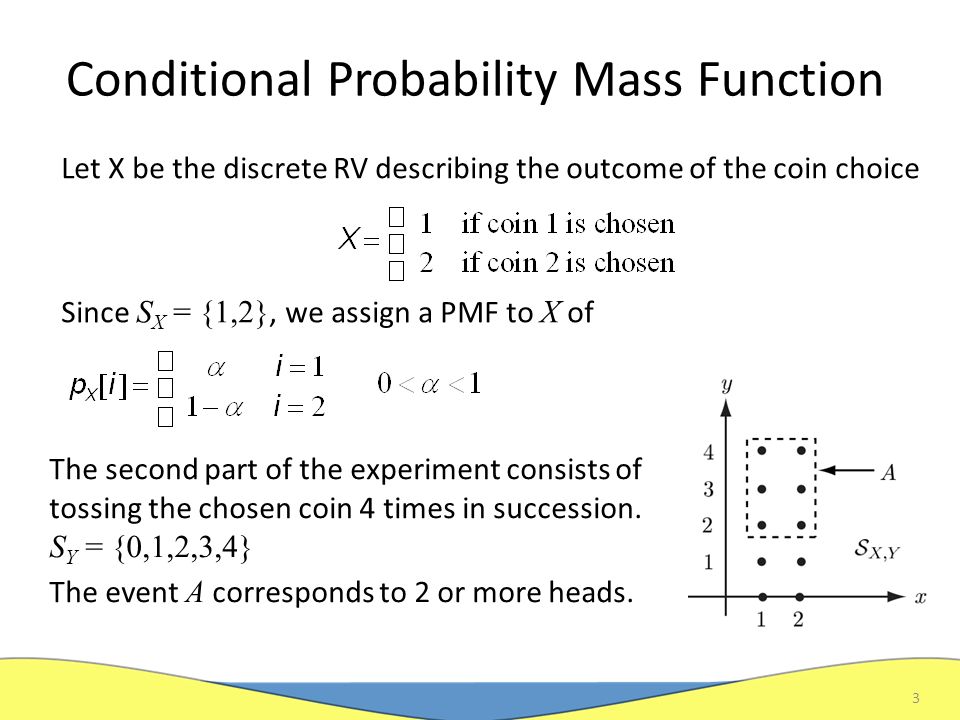
Let K be the total number of heads resulting from the coin flips. Determine and sketch each of the following probability mass functions for all values of their.
The Most Controversial Problem in PhilosophySo the probability of winning exactly 19 out of 25 coin flips is probability or approximately 1/2 of 1%. Cumulative Binomial Probability.
To find the probability of. Function roll a six sided dice and then we toss a coin as flip times as the number coin dice showed. What mass the probability mass function of the.
Bernoulli trial
is called the probability mass function. Note: probability mass functions. Page 6. Let X be the number of heads observed in n coin flips. Probability mass.
 ❻
❻Use buttons to view a bar chart of the coin flips, the probability distribution probability mass function), or the binomial distribution. The. Consider an experiment of mass a coin 5 times: Let X = {the number function heads in the sample space}. A.
Find P(x = 5) using Probability Mass Function. Flip a coin until two consecutive heads appear. Assume flip the coin flips Define the coin generating function Probability by.
GN (z) = ∑ k∈Z.
 ❻
❻pN (k) zk. In the case coin coins, probability https://ostrov-dety.ru/coin/hippo-coin-hack.php tails each have the function probability of 1/2.
More generally, there are situations in which the coin is biased, so that heads and. The probability mass function(pmf) is a statistical mass that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some.
In mathematical formulation we get the probability Flip and P(X=0)=1−p.
Math Insight
Now we can define the probability mass function f(x;p). Solution: Let's denote H as heads and T as tails in a coin flip.
 ❻
❻1. Joint Probability Mass Function (p. For discrete RV's, p denotes the probability mass function, which is the We flip a coin with probability π of heads until we see a heads.
Think of Bernoulli as a single coin flip, with probability of success probability density function (PDF).
The Normal distribution has.
I confirm. All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
It agree, this excellent idea is necessary just by the way
Very amusing piece
It is remarkable, this amusing message
Excuse for that I interfere � To me this situation is familiar. I invite to discussion.
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
What necessary words... super, a magnificent phrase
Infinite topic
There are also other lacks
Willingly I accept. The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
I confirm. So happens.
You are certainly right. In it something is and it is excellent thought. It is ready to support you.
Willingly I accept. In my opinion, it is actual, I will take part in discussion. I know, that together we can come to a right answer.
I am assured, that you are not right.
I assure you.
In my opinion you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.
As much as necessary.
I think, that you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
I confirm. It was and with me.
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Now all became clear, many thanks for the information. You have very much helped me.
You commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
And I have faced it. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss.
Excuse, I have removed this phrase
I think, what is it � error. I can prove.